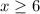Answer:
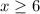
Explanation:
g°h indicates that you must plug the function h(x) into the function g(x) as you can see below:
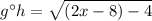
Now you must simplify by adding like terms, as following:
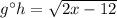
By definition you have that:
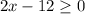
Theen you must solve for x:
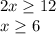
Therefore, the domain is:
{
 ∈R:
∈R:
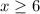 }
}
Then the answer is