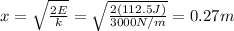Answer:
0.27 m
Step-by-step explanation:
The initial energy of the block (kinetic energy) is given by:
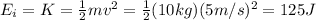
where m=10 kg is the mass of the block and v=5 m/s is the speed.
Later, the block loses 10% of its original energy, so its new energy is 90% of the original energy:
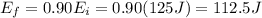
Finally, the block transfers all its kinetic energy to the spring, so the energy is converted into elastic potential energy of the spring, given by
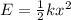
where k=3000 N/m is the spring constant and x is the compression of the spring. Solving for x, we find