Answer:
Obligate aerobic, non-phototrophic organisms will cease to exist due to lack of oxygen for respiration.
Step-by-step explanation:
Phototrophs are organisms that have the capacity to use light to synthesize their foods in a process known as photosynthesis. During this process, phototrophs produce glucose and other carbohydrates using inorganic raw materials such as water and carbon dioxide. Oxygen is liberated in the process.
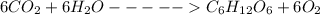
Cellular respiration is the opposite of photosynthesis. The food synthesized during photosynthesis is broken down in the presence of oxygen to release the locked energy which is necessary for proper functioning of organisms. Water and carbon dioxide is produced in the process.
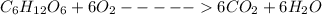
Usually, there is almost always a net glucose production, meaning that photosynthesis rate is always higher than the rate of cellular respiration. This leads to net oxygen production. Aerobic animals depend on this oxygen from autotrophs for their own respiration and energy production.
Hence, if the rate of photosynthesis balances the rate of cellular respiration in phototrophs, there will not be net oxygen production and respiration in obligately aerobic non-autotroph organisms will cease, leading to their non-existence.