(Correct answer choices in boldface)
The total of the three payments comes out to $29000, so
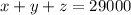
"Two times the first installment is $1000 more than the sum of the third installment and three times the second installment" translates to

The second and third installments have a 15% interest rate, but there's no interest on the first installment. The total interest owed is $2100, so
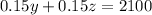
In augmented matrix form, this system is equivalent to
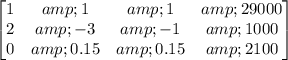
### Row 2, column 1 ### (not row 1, column 1)
The third equation is equivalent to

so the third row in the matrix could adjusted to get
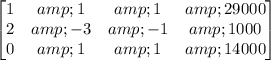
Also, adding the first row to the second gives
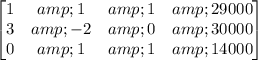
### Row 3, column 2 ### (not row 1, column 2)
Subtracting row 3 from row 1 gives

Subtracting 3 times row 1 from row 2 gives
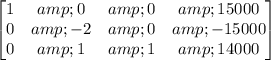
and multiplying row 2 by -1/2 gives
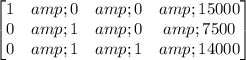
Finally, subtracting row 2 from row 3 gives
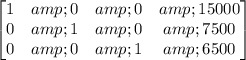
### Row 2, column 3 ### (not row 3, column 2)