Answer:
The vertices of triangle after reflation across x-axis are (1,3), (3,2), (4,5).
The vertices of triangle after reflation across y-axis are (-1,-3), (-3,-2), (-4,-5).
The vertices of triangle after reflation across y=x are (-3,1), (-2,3), (-5,4).
Explanation:
From the given figure it is clear that the vertices of triangle are (1,-3), (3,-2), (4,-5).
If a figure reflected over the x-axis, then
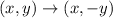
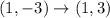
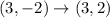
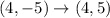
The vertices of triangle after reflation across x-axis are (1,3), (3,2), (4,5).
If a figure reflected over the y-axis, then
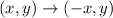
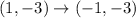
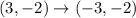
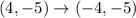
The vertices of triangle after reflation across y-axis are (-1,-3), (-3,-2), (-4,-5).
If a figure reflected over the y=x, then
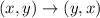
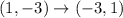
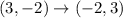
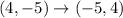
The vertices of triangle after reflation across y=x are (-3,1), (-2,3), (-5,4).