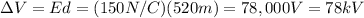(a)
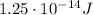
The change in potential energy of the electron is given by:
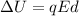
where
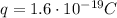 is the magnitude of the electron's charge
is the magnitude of the electron's charge
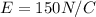 is the magnitude of the electric field
is the magnitude of the electric field
d = 520 m is the distance through which the electron has moved
Substituting into the equation, we find
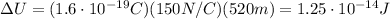
(b) 78 kV
The potential difference the electron has moved through is given by
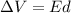
where
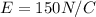 is the magnitude of the electric field
is the magnitude of the electric field
d = 520 m is the distance through which the electron has moved
Substituting into the equation, we find