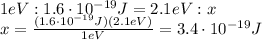Answer:
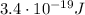
Step-by-step explanation:
In order to convert the work function of cesium from electronvolts to Joules, we must use the following conversion factor:
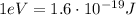
In our problem, the work function of cesium is
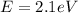
so, we can convert it into Joules by using the following proportion: