The unknown temperature (T2) is approximately -14.4 degrees Celsius.
Charles's law states that for a fixed amount of gas at constant pressure, the volume is directly proportional to the absolute temperature. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
V1/T1 = V2/T2
Since the pressure is constant in this scenario (P1 = P2), we can assume the volume remains the same (V1 = V2).
Therefore, the equation simplifies to:
T2 = T1 * (P2 / P1)
T1 = -84 °C
P1 = 8.33 * *
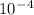 atm
atm
P2 = 3.92 * atm
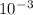
T2 = (-84 °C + 273.15) * (3.92 *
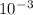 atm / 8.33 * atm)
atm / 8.33 * atm)
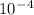
T2 = -14.4 °C
complete question:
Calculate the unknown quantity in each of the following measurements of gases.
P1 = 8.33 * 10^-4 atm
T1 = -84 degrees C
P2 = 3.92 * 10^-3 atm
T2 = ? degrees C