Final answer:
The probability of at least one reaction when yeast is added to two flasks, when four out of six flasks contain hydrogen peroxide, is approximately 93.33%.
Step-by-step explanation:
The student's science experiment involves calculating the probability of a chemical reaction occurring when yeast is added to hydrogen peroxide. In this case, the reaction being referred to is:
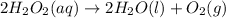
Since the student has six flasks and yeast is added to only two, the probability calculation relies on knowing which flasks contain hydrogen peroxide, because these are the flasks where a reaction could occur. There are four flasks with hydrogen peroxide, so the probability of at least one reaction occurring is contingent on whether any of these four are chosen for yeast addition. We calculate the probability of no reaction occurring first, which can only happen if both flasks with water are chosen. As there are 2 water flasks and 4 peroxide flasks, the probability of picking a water flask first is 2/6, and if successful, picking the second water flask is 1/5. Multiplying these together gets the probability of no reaction occurring, which is 2/6 * 1/5 = 2/30 or 1/15. To find the probability of at least one reaction occurring, we subtract this from 1. Thus, the probability of at least one reaction occurring is 1 - 1/15 = 14/15 or approximately 93.33%.