Answer:
the coefficient of static friction between the puck and the surface
Step-by-step explanation:
As per the FBD we can say that as we increase the angle of the inclination the component of force of gravity will counterbalance the friction force
At the condition of just equilibrium when it is just begin to slide then in that case we can say
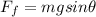
so here for finding frictional force maximum value we can say
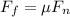
here for finding Normal force we can write force balance normal to the inclined plane
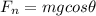
now from above equations
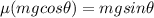
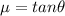
so angle depends on the coefficient of static friction