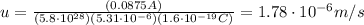1) Current in the wire: 0.0875 A
The current in the wire is given by:
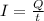
where
Q is the charge passing a given point in the conductor
t is the time elapsed
In this problem, we have
Q = 420 C is the total charge passing through a given point in a time of
t = 80 min = 4800 s
So, the current is
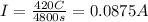
2) Drift velocity of the electrons:
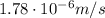
The drift velocity of the electrons in the wire is given by:
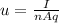
where
I = 0.0875 A is the current
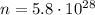 is the number of free electrons per cubic meter
is the number of free electrons per cubic meter
A is the cross-sectional area
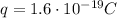 is the charge of one electron
is the charge of one electron
The radius of the wire is
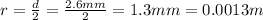
So the cross-sectional area is
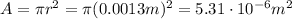
So, the drift velocity is