Answer:
constant acceleration
Step-by-step explanation:
An object is said to be in free fall when only one force is acting on it: the force of gravity, which pushes the object towards the ground.
Newton's second law states that the resultant of the forces acting on an object is equal to the product between the mass of the object (m) and its acceleration:
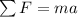 (1)
(1)
for an object in free fall, there is only one force, the force of gravity:
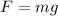
where g = 9.8 m/s^2 is the gravitational acceleration. Substituting this into (1), we have
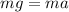
and so
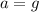
which means that the object is moving at constant acceleration downward, with acceleration equal to g = 9.8 m/s^2.