Answer:
a) α = 0.0334 rad / s² , b) w = 2.14 rad/s see that the angular velocity doubles.
Step-by-step explanation:
This is a magular kinematics exercise
Let's reduce the magnitudes to the SI system
w = 0.17 rev /s (2π rad / 1rev) = 1.07 rad / s
a) as part of rest its initial velocity is zero w or = 0
w = w₀ + α t
α =
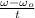
α =
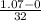
α = 0.0334 rad / s²
b) If we double the angular relation what will be the final velocity
w = w₀ + (2α) t
w = 0 + 2 0.0334 32
w = 2.14 rad/s
We see that the angular velocity doubles.