HA in the graph represents a weak acid.
Explanation
Is HA an acid or a base?
Apply the Arrhenius Theory of Acids and Bases.
- Acids ionize in water to produce
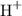 (or equivalently
(or equivalently
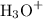 ) and a conjugate ion.
) and a conjugate ion. - Bases ionize in water to produce
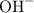 and a conjugate ion.
and a conjugate ion.
The equation in the picture shows that HA ionizes in water to produce
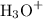 ions. By the Arrhenius Theory of acids and bases, HA is an acid.
ions. By the Arrhenius Theory of acids and bases, HA is an acid.
Is HA a weak acid or a strong acid?
Both weak and strong Arrhenius acids ionize in water to produce
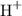 (or equivalently
(or equivalently
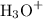 ) and a conjugate ion. However,
) and a conjugate ion. However,
- Strong acids ionize completely. There would be nearly no acid left in the solution. Expect arrows
 ⇒ in only one direction in the equation.
⇒ in only one direction in the equation. - Weak acids also ionize, but only partially. There would be plenty of acid left in the solution. Expect two-sided arrows like ⇔ and two-sided harpoons like
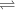 in the equation.
in the equation.
As seen in the bar chart, there are plenty of HA left after ionization. HA ionizes only partially. Also, the equation shows a two-sided arrow. As a result, HA is a weak acid.