Answer:
Domain:All real numbers except x≠3 and x≠ -1/2,V.A= x=3 , x= -1/2.root=5,y-int= 5/3.H.A=0 , no hole , no O.A.
Explanation:
We have given the function:
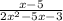
So, first we simplify the equation we get,
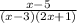
We have to find the domain :
Domain is the value of x for which the function is defined.
For this, denominator must not be equal to zero.
(x-3)(2x+1) ≠ 0
(x-3)≠0 , (2x+1)≠0
x≠3 , x≠ -1/2
So, the domain is all real numbers except x≠3 and x≠ -1/2.
For vertical asymptotes, denominator is equal to zero.
(x-3)(2x+1) = 0
x=3 , x= -1/2 are vertical asymptotes.
Nominator is equal to zero for roots:
x-5 = 0
x= 5 is the root.
Put x = 0 for y-intercept:
y = 0-5/(0-3)(2(0)+1)
y = 5/3 is the y-intercept.
Horizontal asymptote is :
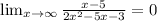
Horizontal asymptote is y = 0.
The function has no hole because it is reducible.
It has no oblique asymptote because it is proper function.
Graph is attached.