Hello!
The answers are:
Height to achieve a speed of 2 m/s = 0.20m
Height to achieve a speed of 3 m/s = 0.46m
Height to achieve a speed of 4 m/s = 0.82m
Height to achieve a speed of 5 m/s = 1.28m
Height to achieve a speed of 6 m/s = 1.84m
Why?
Since an object in free fall is accelerated by gravity, the speed will increase according to the distance where the object is dropped. Gravitational acceleration is equal to 9.8 m/s2, it means that the speed will be increased by 9.8 m/s each second.
We are asked to find the heights necessary to drop the bottle to achieve the given speeds, so:
Speed of 2 m/s calculations:
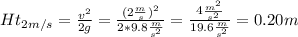
Speed of 3 m/s calculations:
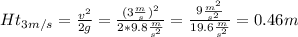
Speed of 4 m/s calculations:
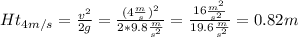
Speed of 5 m/s calculations:
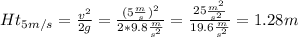
Speed of 6 m/s calculations:
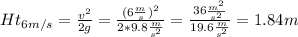
Have a nice day!