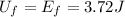Answer:
3.72 J
Step-by-step explanation:
Neglecting air resistance, the mechanical energy of the stone is conserved. Therefore, the mechanical energy at the starting point of the trajectory will be equal to the mechanical energy at the maximum height:
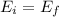
The mechanical energy at the starting point is sum of kinetic energy and potential energy:
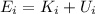
where:
- the initial kinetic energy of the stone is
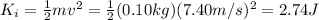
- the initial potential energy of the stone is
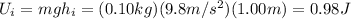
So the initial mechanical energy is
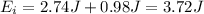
The mechanical energy at the maximum height will be the same:
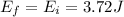
And it is the sum of kinetic and potential energy:
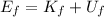
however, at the point of maximum height the velocity of the stone is zero; therefore, its kinetic energy is zero:
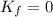 , and so the potential energy is simply equal to the mechanical energy:
, and so the potential energy is simply equal to the mechanical energy: