Answer:
The power dissipated is reduced by a factor of 2
Step-by-step explanation:
The power dissipated by a resistor is given by:
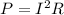
where
I is the current
R is the resistance
by using Ohm's law,
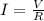 , we can rewrite the previous equation in terms of the voltage applied across the resistor (V):
, we can rewrite the previous equation in terms of the voltage applied across the resistor (V):
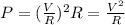
In this problem, the resistance of the element is doubled, while the voltage is kept constant. So we have
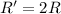 while V remains the same; substituting into the formula, we have:
while V remains the same; substituting into the formula, we have:
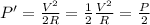
so, the power dissipated is reduced by a factor 2.