For this case we have that, by definition, the domain of a function is given by all the values for which the function is defined.
Having said that, we have the following function:
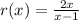
It is not defined when the denominator is equal to 0. That is:
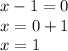
Thus, the domain of r (x) is given by all real numbers except 1.
Answer:
all real numbers except 1.
Option A