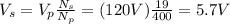1.
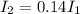
Step-by-step explanation:
We have:
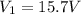 voltage in the primary coil
voltage in the primary coil
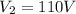 voltage in the secondary coil
voltage in the secondary coil
The efficiency of the transformer is 100%: this means that the power in the primary coil and in the secondary coil are equal
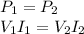
where I1 and I2 are the currents in the two coils. Re-arranging the equation, we find
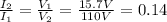
which means that the current in the secondary coil is 14% of the value of the current in the primary coil.
2. 5.7 V
We can solve the problem by using the transformer equation:
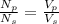
where:
Np = 400 is the number of turns in the primary coil
Ns = 19 is the number of turns in the secondary coil
Vp = 120 V is the voltage in the primary coil
Vs = ? is the voltage in the secondary coil
Re-arranging the formula and substituting the numbers, we find: