If we check prime numbers, we can see that only 2 and 5 produce a fraction with a finite number of decimal digits:
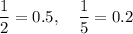
All other primes produce fractions with periodic, infinite decimal expansions.
So, if the prime factorization of the denominator only contains 2 and 5, the fraction will have a finite decimal expansion.
In fact:
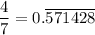
because the prime factorization of the denominator contains 7.
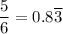
because the prime factorization of the denominator contains 2, but also 3.
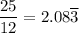
because the prime factorization of the denominator contains 2, but also 3.
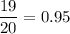
because the prime factorization of the denominator only contains 2 and 5.