Answer : The colligative property employed to achieve this can be, Elevation in boiling point.
Explanation :
Elevation in boiling point : It is defined as the temperature or boiling point of a liquid (a solvent) will be higher when the another compound is added. This means that a solution must be at a higher temperature or boiling point than a pure solvent.
For example : When a non-volatile solute (a salt) is added to a pure solvent such as water.
The formula for elevation in boiling point will be,
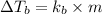
or,
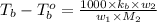
where,
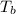 = boiling point of solution
= boiling point of solution
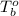 = boiling point of pure solvent
= boiling point of pure solvent
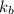 = boiling point constant
= boiling point constant
m = molality
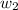 = mass of solute
= mass of solute
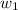 = mass of solvent
= mass of solvent
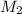 = molar mass of solute
= molar mass of solute
Hence, the colligative property employed to achieve this can be, Elevation in boiling point.