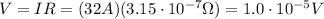Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
First of all, we need to calculate the resistance of the piece of copper wire between the bird's feet, which is given by
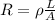
where:
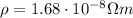 is the resistivity of copper
is the resistivity of copper
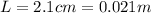 is the length of the piece of wire between the bird's feet
is the length of the piece of wire between the bird's feet
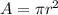 is the cross-sectional area of the wire, with r being the radius. Since the radius is half the diameter:
is the cross-sectional area of the wire, with r being the radius. Since the radius is half the diameter:
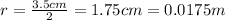
the area is
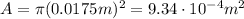
And the resistance is
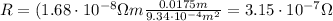
And given the current in the wire, I=32 A, we can calculate the potential difference across the bird's body by using Ohm's law: