Answer:
1)
a)
We are given one leg of triangle as 6 km and the other leg is of length of 8 km.
Hence, the hypotenuse is calculated using Pythagorean theorem as:
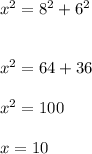
Hence, the hypotenuse of the triangle or the missing side x=10 cm.
Now we calculate trignometric ratio with respect to angle a and b as:
b)
We know that:
Sine of an angle is ratio of perpendicular to hypotenuse.
Cosine of an angle is ratio of base and hypotenuse.
And tangent of an angle is ratio of perpendicular and base.
Angle a:
We have perpendicular=8
Base=6
Hypotenuse=10
Hence,
sin a=8/10
cos a=6/10
tan a=8/6
Angle b:
Perpendicular =6
Base=8
Hypotenuse=10
Hence,
sin b=6/10
cos b=8/10
tan b=6/8