Answer:
Concentration of HCl =
 = 0.075L= 75mL
= 0.075L= 75mL
Concentration of KOH =
 = 0.0056L = 5.6mL
= 0.0056L = 5.6mL
Concentration of H₂SO₄ =
 = 0.108L = 108mL
= 0.108L = 108mL
Step-by-step explanation:
Procedure
This a problem related to volumetric analysis and we need to find the concentrations of the acids involved in the neurtralization process.
In order to determine the concentrations, we work from the known reactants to the unknown reactants or products.
1. Write the balanced equation of the reactions
2. List the given parameters and work from the known to the unknown. The known is that specie that can give us the number of moles required for this reaction.
3. Check the parameters and make sure that they are in their appropriate units.
4. Obtain the number of moles of the known using the concentration and volume of the reactant using the equation below:
Number of moles = Concentration x Volume.
5. Using the known number of moles, determine that of the unknown by comparing their mole ratios.
6. Since we have obtained the number of moles of the unknown, we can then solve for the concentration of the unknown using the expression below:

Solution
1. If it takes 67 mL of 0.15 M NaOH to neutralize 134 mL of an HCl solution, what is the concentration of the HCl?
Given parameters:
Volume of base NaOH = 67mL to litres = 67 x 10⁻³ = 0.067L
Concentration of NaOH = 0.15M
Volume of acid HCl = 134mL = 134 x 10⁻³ = 0.134L
Concentration of acid = ?
Equation of reaction: NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H₂O
The known here is the base, NaOH.
Using:
Number of moles of NaOH = Concentration of NaOH x Volume of NaOH
Number of moles of NaOH = 0.15M x 0.067L = 0.01mol
From the equation of the reaction, we know that;
1mole of NaOH reacted with 1mole of HCl
Therefore, 0.01 mole of HCl would also react with 0.01 of NaOH
Now that we know the number of moles HCl, we can now obtain the concentration of HCl required to neutralize NaOH using the equation below:
Concentration of HCl =

Concentration of HCl =
 = 0.075L= 75mL
= 0.075L= 75mL
2. If it takes 27.4 mL of 0.050 M H₂SO₄ to neutralize 357 mL of KOH solution, what is the concentration of the KOH solution?
Given parameters:
Concentration of H₂SO₄ = 0.05M
Volume of acid H₂SO₄ = 27.4mL = 27.4 x 10⁻³ = 0.0274L
Volume of base KOH = 357mL to litres = 357 x 10⁻³ = 0.357L
Concentration of KOH = ?
Equation of reaction: 2KOH + H₂SO₄ → K₂SO₄ + 2H₂O
The known here is the acid, H₂SO₄
Using:
Number of moles of H₂SO₄ = Concentration of H₂SO₄ x Volume of H₂SO₄
Number of moles of H₂SO₄ = 0.05M x 0.0274L = 0.001mol
From the equation of the reaction, we know that;
2moles of KOH reacted with 1mole of H₂SO₄
Therefore, 0.001 mole of H₂SO₄ would also react with 0.002 of KOH
Now that we know the number of moles KOH, we can now obtain the concentration of KOH required to neutralize H₂SO₄ using the equation below:
Concentration of KOH =

Concentration of KOH =
 = 0.0056L = 5.6mL
= 0.0056L = 5.6mL
3. If it takes 55 mL of 0.5 M NaOH solution to completely neutralize 130 mL of sulfuric acid solution H₂SO₄, what is the concentration of the H₂SO₄ solution?
Given parameters:
Volume of base NaOH = 55mL to litres = 55 x 10⁻³ = 0.055L
Concentration of NaOH = 0.5M
Concentration of H₂SO₄ = ?
Volume of acid H₂SO₄ = 130mL = 130 x 10⁻³ = 0.13L
Equation of reaction: 2NaOH + H₂SO₄ → Na₂SO₄ + 2H₂O
The known here is the base, NaOH
Using:
Number of moles of NaOH = Concentration of NaOH x Volume of NaOH
Number of moles of NaOH = 0.5M x 0.055L = 0.028mol
From the equation of the reaction, we know that;
2moles of NaOH reacted with 1mole of H₂SO₄
Therefore, 0.028 mole of NaOH would also react with
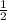 of 0.028, 0.014mole of H₂SO₄
of 0.028, 0.014mole of H₂SO₄
Now that we know the number of moles H₂SO₄, we can now obtain the concentration of H₂SO₄ required to neutralize NaOH using the equation below:
Concentration of H₂SO₄ =

Concentration of H₂SO₄ =
 = 0.108L = 108mL
= 0.108L = 108mL