Answer: The correct statement is low temperature only, because entropy decreases during freezing.
Step-by-step explanation:
The relationship between Gibb's free energy, enthalpy, entropy and temperature is given by the equation:
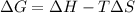
Where,
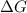 = change in Gibb's free energy
= change in Gibb's free energy
 = change in enthalpy
= change in enthalpy
T = temperature
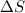 = change in entropy
= change in entropy
It is given that freezing of methane is taking place, which means that entropy is decreasing and
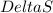 is becoming negative. It is also given that the reaction is an exothermic reaction, this means that the
is becoming negative. It is also given that the reaction is an exothermic reaction, this means that the
 is also negative.
is also negative.
For a reaction to be spontaneous,
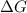 must be negative.
must be negative.
![-ve=-ve-[T(-ve)]\\\\-ve=-ve+T](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/z75kyotx6gph2r2u7wkvmd32p2yztkg41f.png)
From above equations, it is visible that
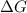 will be negative only when the temperature will be low.
will be negative only when the temperature will be low.
Hence, the correct statement is low temperature only, because entropy decreases during freezing.