PART A)
Impulse is defined as change in momentum
here finally after hitting the wall car comes to rest
So final momentum of the car will be ZERO
Initial momentum of the car is given as
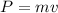
here m = 2000 kg
v = 77 m/s
now we have
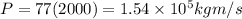
so here impulse will be
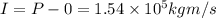
PART B)
As we know that force of impact is defined as
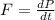
so here it is ratio of impulse and time
so if we increase the time of impact by 3 times
so the force will be decrease by factor of 1/3
so here force is decreased by 1/3