Answer:
The velocity of gas molecules is proportional to their Kelvin temperature.
Step-by-step explanation:
The average velocity of the gas molecules is directly proportional to the Kelvin temperature which is given by:
v =
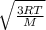
where v, R, T and M are the velocity of the gas, R is the universal gas constant, T is the absolute temperature in Kelvin and M is the molar mass of the gas.
As the temperature is lowered the velocity of the gas particles simultaneously lowers and the balloon collapses.