Answer:
Mass on Mars = 18 kg (remain same as on earth ) and
Weight on Mars = 66.6 Newtons (Decreases as compared to weight on earth)
Step-by-step explanation:
(a)
>Since mass is the intrinsic property of any object it will not change at any place and remain constant irrespective of planet where it is measured .
>Mass is the quantity of matter in a body regardless of its volume or of any forces acting on it. The term should not be confused with weight, which is the measure of the force of gravity acting on a body .
Thus the mass of the robot on the earth and Mars will be same and is equal to 18 kg . (remain constant)
(b)
Weight is the measure of the force of gravity applied on the object(robot in this case) by the given planet (Mars in this case) .
=> Weight (W)= Mass(m)x Acceleration due to gravity of Mars(
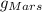 )
)
=>
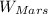 = m
= m
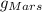 = (18x3.7) N = 66.6 Newtons
= (18x3.7) N = 66.6 Newtons
While on earth the value of acceleration due to gravity is
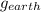 =9.8
=9.8
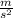
So weight on earth is
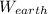 = (18x9.8) N= 176.4 Newtons
= (18x9.8) N= 176.4 Newtons
Thus the weight of robot will decrease on Mars as compared to weight on earth .