Answer: Option (b) is the correct answer.
Step-by-step explanation:
- Dipole-dipole interactions are defined as the interactions that occur when partial positive charge on an atom is attracted by partial negative charge on another atom.
For example, hydrocarbons show dispersion forces due to difference in the electronegativity of its combining atoms.
- The weak intermolecular forces which can arise either between nucleus and electrons or between electron-electron are known as dispersion forces. These forces are also known as London dispersion forces.
- When a hydrogen atom is bonded to a larger atom then the weak force which exists between the hydrogen and another atom is known as hydrogen bonding.
A hydrogen bond will only exist if a compound has N. O, F atoms attached to the hydrogen atom.
Order of some forces in the order of increasing strength is as follows.
Dispersion forces < dipole-induced dipole < dipole-dipole < hydrogen bonding < ion-dipole
In
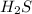 molecule there will be no hydrogen bonding because there is no nitrogen, oxygen and fluorine atom.
molecule there will be no hydrogen bonding because there is no nitrogen, oxygen and fluorine atom.
But due to the difference in electronegativities of hydrogen and sulfur atom, there will be partial opposite charges on both the atoms. Hence, dipole-dipole forces will exist between the two.
Thus, we can conclude that dipole-dipole force is the strongest intermolecular force that occurs between molecules of
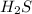 .
.