Answer:
When original wave superimpose with its own reflected wave travelling in opposite direction then it will produce standing wave
Step-by-step explanation:
Let say the equation of original wave is
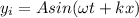
now the equation of its reflected wave which is reflected 100% is given as
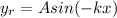
now by superposition of above two waves we will have
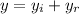
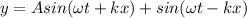
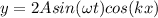
so above shows the equation of standing wave
so we can say that When original wave superimpose with its own reflected wave travelling in opposite direction then it will produce standing wave