Temperature of the same cup of water will rise by 6 °C unless it boils.
Step-by-step explanation
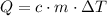 .
.
However, neither
 nor
nor
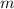 is given.
is given.
Adding
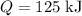 to this cup of water of mass
to this cup of water of mass
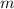 rises its temperature by
rises its temperature by
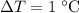 .
.
In other words,
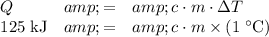
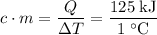 .
.
Both
 and
and
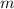 are constant for the same cup of water unless the water boils. It's possible to reuse the value of
are constant for the same cup of water unless the water boils. It's possible to reuse the value of
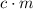 in the second calculation. Here's how:
in the second calculation. Here's how:
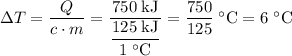 .
.