Answer:
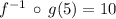
Explanation:
Let
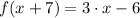 and
and
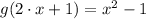 , we proceed to derive
, we proceed to derive
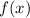 and
and
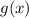 by algebraic means:
by algebraic means:
(i)
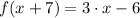
1)
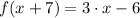 Given
Given
2)
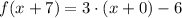 Modulative property
Modulative property
3)
![f(x+7) = 3\cdot [(x+7) +(-7)]-6](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/7dziza0enw92ih3d1grzqw64u4yxaqxd5u.png) Existence of additive inverse/Associative property
Existence of additive inverse/Associative property
4)
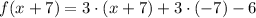 Distributive property
Distributive property
5)
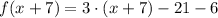
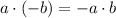
6)
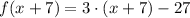 Definition of subtraction
Definition of subtraction
7)
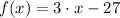 Composition of functions/Result
Composition of functions/Result
(ii)
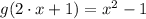
1)
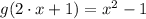 Given
Given
2)
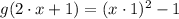 Modulative property
Modulative property
3)
![g(2\cdot x +1) = [(2\cdot x)\cdot 2^(-1)]^(2)-1](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/50b1vpeby6uq00hgquudm4gfxtp1z25f99.png) Existence of additive inverse/Commutative and associative properties
Existence of additive inverse/Commutative and associative properties
4)
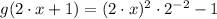
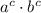 /
/
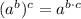
5)
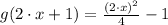 Definitions of division and power
Definitions of division and power
6)
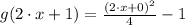 Modulative property
Modulative property
7)
![g(2\cdot x +1) = ([(2\cdot x + 1)+(-1)]^(2))/(4) -1](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/s2lo0js9hfvkka8ocvcc71wtlwcpykzz0j.png) Existence of additive inverse/Associative property
Existence of additive inverse/Associative property
8)
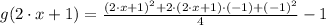 Perfect square trinomial
Perfect square trinomial
9)
![g(2\cdot x + 1) = ((2\cdot x + 1)^(2))/(4)+([2\cdot (-1)]\cdot (2\cdot x + 1))/(4) +((-1)^(2))/(4)-1](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/op677sf0nztscxfkg5u0z8bvwsz5no812n.png) Addition of homogeneous fractions.
Addition of homogeneous fractions.
10)
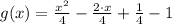 Composition of functions/
Composition of functions/
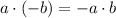
11)
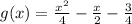 Definitions of division and subtraction/Result
Definitions of division and subtraction/Result
Now we find the inverse of
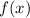 :
:
1)
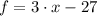 Given
Given
2)
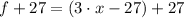 Compatibility with addition
Compatibility with addition
3)
![f+ 27 = 3\cdot x +[27+(-27)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/lyuc81mj9yt8qz67pvrf6duh1svxkknucq.png) Definition of substraction/Commutative and associative properties
Definition of substraction/Commutative and associative properties
4)
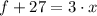 Existence of additive inverse/Modulative property
Existence of additive inverse/Modulative property
5)
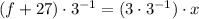 Compatibility with multiplication/Commutative and associative properties
Compatibility with multiplication/Commutative and associative properties
6)
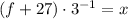 Existence of multiplicative inverse/Modulative property
Existence of multiplicative inverse/Modulative property
7)
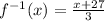 Symmetrical property/Notation/Result
Symmetrical property/Notation/Result
Finally, we proceed to calculate
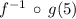 :
:
1)
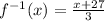 ,
,
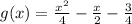 Given
Given
2)
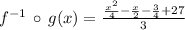 Composition of functions
Composition of functions
3)
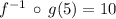 Result
Result