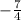Answer:
g(-3) =
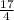
g(2) = -3
g(5) =
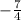
Explanation:
Let us solve the question
∵ g(x) =
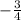 x + 2, x ≠ 2
x + 2, x ≠ 2
→ That means we can use it for any value os x except 2
∵ g(x) = -3, x = 2
→ That means we will use it only if x = 2
We want to find g(-3)
∵ x = -3 ⇒ ≠ 2
∴ We will use g(x) =
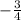 x + 2
x + 2
→ Substitute x by -3
∵ g(-3) =
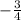 (-3) + 2
(-3) + 2
∴ g(-3) =
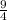 + 2
+ 2
∴ g(-3) =
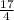
We want to find g(2)
∵ x = 2
∴ We will use g(x) = -3
→ This is a constant function which means g(2) equal to -3
∴ g(2) = -3
We want to find g(5)
∵ x = 5 ⇒ ≠ 2
∴ We will use g(x) =
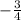 x + 2
x + 2
→ Substitute x by 5
∵ g(5) =
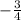 (5) + 2
(5) + 2
∴ g(5) =
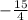 + 2
+ 2
∴ g(5) =