Step-by-step explanation:
Volume of fuel used per hour = 1 gal /h
1 gal =
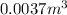
Mass of the fuel =
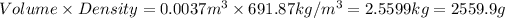
Moles of isoactane:
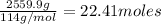
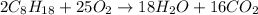
2 moles of iso-octane react with 25 moles of oxygen then 22.41 moles of iso-octane will react with :
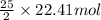 of oxygen that is 280.125 moles.
of oxygen that is 280.125 moles.
We are given that Air contains 21 mole % of oxygen:
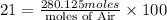
Moles of Air =1333.92 moles
Feed rate of the air = 1333.92/h
Ratio of gasoline to air being fed to engine:
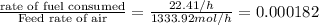
If the ratio gasoline to air is less than or equal to 0.000749 than no accumulation of CO will be there in an engine.
The CO got accumulated in the engine which means that ratio of gasoline to air is greater than the 0.000749.