Answer:
The possible zeroes are -3 , -5/3 and 1/2
Explanation:
* To find the zeroes you must let f(x) = 0
* First step look at the numerical term -15 then find two numbers multiply by each other and = -15⇒[ (5×-3) (-5×3) (-1×15) (1×-15)] and let x = one of them
* Second step Chose on of them and substitute x by it, I will chose -3
* f(-3) =
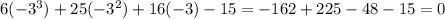
∵ f(x) = 0 when x = -3
∴ x + 3 is a factor of f(x)
* Third step divide f(x) by its factor to get quadratic and factorize it
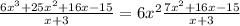
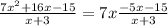
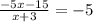
∴ f(x) = (x + 3)(
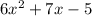 ⇒factorize the quadratic
⇒factorize the quadratic
∵f(x) = (x + 3)(2x - 1)(3x + 5)
∵ f(x) = 0
∴ x + 3 = 0 ⇒ x = -3
∴ 2x - 1 = 0 ⇒ x = 1/2
∴ 3x + 5 = 0 ⇒ x = -5/3
∴