Answer:
Charles Law: V/T = constant
Step-by-step explanation:
The ideal gas equation relates the pressure (P), temperature (T) and volume (V) of 'n' moles of a gas through the following equation:
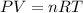
where R = universal gas constant = 0.0821 Latm/mol-K
As per the kinetic molecular theory, an increase in temperature will increase the kinetic energy of the gas particles thereby increasing the rate of collision. Under constant pressure conditions, the volume would have to increase so as to reduce the rate of collisions. This implies that the volume (V) is directly proportional to the temperature (T).
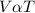
i.e.
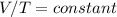
This is referred to as Charles' Law