860 mL.
Step-by-step explanation
Separate this process into two steps:
- Cool the balloon from 305 K to 265 K.
- Reduce the pressure on the balloon from 0.45 atm to 0.25 atm.
What would be the volume of the balloon after each step?
After Cooling the balloon at constant pressure:
By Charles's Law, the volume of a gas is directly related to its temperature in degrees Kelvins.
In other words,
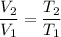 ,
,
where
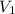 and
and
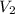 are volumes of the same gas.
are volumes of the same gas.
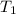 and
and
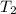 are the temperatures (in degrees Kelvins) of that gas.
are the temperatures (in degrees Kelvins) of that gas.
Rearranging,
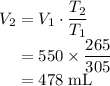 .
.
The balloon ended up with a lower temperature. As a result, its volume drops:
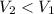 .
.
After reducing the pressure on the balloon at constant temperature:
By Boyle's Law, the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to the pressure on this gas.
In other words,
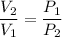 ,
,
where
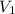 and
and
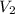 are volumes of the same gas.
are volumes of the same gas.
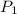 and
and
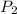 are the pressures on this gas.
are the pressures on this gas.
Rearranging,
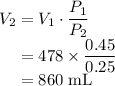 .
.
There's now less pressure on the balloon. As a result, the balloon will gain in volume:
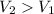 .
.
The final volume of the balloon will be
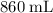 .
.