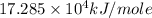Answer : The activation energy of the reaction is,
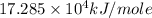
Solution :
The relation between the rate constant the activation energy is,
![\log (K_2)/(K_1)=(Ea)/(2.303* R)* [(1)/(T_1)-(1)/(T_2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ggk6vasjx91pdnajaj81ch8aqcw1i6hzdw.png)
where,
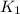 = initial rate constant =
= initial rate constant =
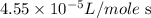
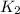 = final rate constant =
= final rate constant =
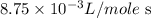
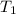 = initial temperature =
= initial temperature =
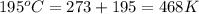
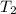 = final temperature =
= final temperature =
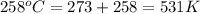
R = gas constant = 8.314 kJ/moleK
Ea = activation energy
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get the activation energy.
![\log \frac{8.75* 10^(-3)L/mole\text{ s}}{4.55* 10^(-5)L/mole\text{ s}}=(Ea)/(2.303* (8.314kJ/moleK))* [(1)/(468K)-(1)/(531K)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/bnfmraobs3h1jx0p8tdsj8kcmho9mi47r0.png)
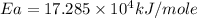
Therefore, the activation energy of the reaction is,