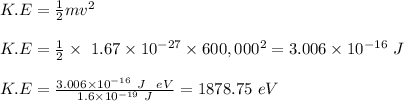Answer:
(1) the potential difference that stopped the proton is 1878.75 V
(2) the initial kinetic energy of the proton is 1878.75 eV
Step-by-step explanation:
Given;
initial speed of the proton, v = 600,000 m/s
mass of proton, m = 1.67 x 10⁻²⁷ kg
(1) The work done in bringing the proton to rest is given as;
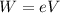
Apply work energy theorem;
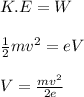
where;
V is the potential difference
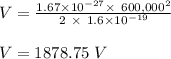
(2) the initial kinetic energy of the proton, in electron volts;