Answer:
From the test give in the question it is obvious that there is enough evidence to show that population mean varies for vegetarian and non-vegetarian
The P-value helps affirm the null hypothesis claims,The P-value attains values relatively as large as that which exists in the sample given,if the null hypothesis is right
Explanation:
From the question we are told that
Sample mean
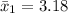
Standard deviation
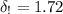
Sample size
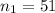
Sample mean
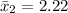
Standard deviation
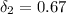
Sample size
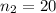
Generally this is a two tailed test
therefore
Null hypothesis =
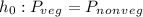
Alternative hypothesis
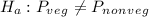
From the test give in the question it is obvious that there is enough evidence to show that population mean varies for vegetarian and non-vegetarian
The P-value helps affirm the null hypothesis claims,The P-value attains values relatively as large as that which exists in the sample given,if the null hypothesis is right