Answer:
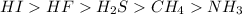
Step-by-step explanation:
Let's remember the definition of a Bronsted-Lowry acid: Is a molecule that has the capacity to produce the hydronium ion
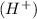 .
.
A few examples of acids compounds are:
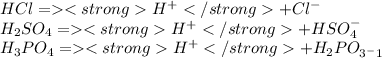
Now, the capacity of a compound to produce the hydronium would higher if the bond between the atom and the hydrogen is weaker. In other words: if the bond X- H (where X is any atom) is weaker would be more easy to produce the hydronium ion and therefore we will have a strongest acid.
The weakening of the bond can be due to 2 properties, electronegativity and atomic radius. As for the electronegativity goes, is necessary to check the electronegativity difference between the atoms. If we have a higher electronegativity difference the bond would be more polarized, in other words a weaker X-H bond and therefore more acidic.
The other property is the atomic radius if we have a bigger atom (larger atomic radius) the bond would be weaker and therefore more acidic. The atomic radius trend in the periodic table is.
That’s why the HI is the most acidic compound, it has the largest atomic radius, therefore, is more acidic compound. Next, using the electronegativity difference concept we can rank HF, H2S, and CH4. Finally, for NH3 we have a special case because this compound is a base (the opposite to the acids), so, instead of producing hydronium ions will remove H+ from the solution and therefore will have the weakest acidity of all the compounds.