Answer: When evaporation occurs, the osmotic pressure increases.
Step-by-step explanation:
Osmotic pressure is defined as the minimum excess pressure that can be applied on the solution to prevent the entry of the solvent into the solution through a semipermeable membrane. The formula to calculate osmotic pressure is given by the equation:
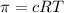
where,
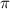 = osmotic pressure
= osmotic pressure
c = concentration of solute
R = gas constant
T = temperature
As, concentration of solute is directly proportional to the osmotic pressure. So, when concentration increases, osmotic pressure also increases and vice-versa.
Evaporation is a process when liquid changes its state to gaseous state by increasing the temperature. In this process, solvent particles escape and more and more solute particles remain in the solution. So, concentration of solute particles increases.
Hence, evaporation causes increase in the osmotic pressure.