Answer :
Strong electrolyte solutes are BD and PR.
Weak electrolyte solute is AC.
Non-electrolyte solutes are M and N.
Explanation :
Strong electrolyte : It is defined as the species that can completely dissociates into ions in its aqueous solution.
Weak electrolyte : It is defined as the species that is partially dissociates into ions in its aqueous solution.
Non-electrolyte : It is defined as the species that does not dissociates into ions in its aqueous solution.
As we are given the following reactions. Now we have to determine the solute as a strong electrolyte, a weak electrolyte, or a non-electrolyte.
(1)
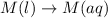
In this reaction, there is no dissociation into ions. So, It is a non-electrolyte.
(2)
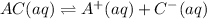
In this reaction, the partial dissociation into ions and equilibrium arrow represent the incomplete dissociation. So, it is a weak electrolyte.
(3)
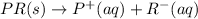
In this reaction, the complete dissociation into ions and only onside arrow represent the completely dissociated. So, it is a strong electrolyte.
(4)
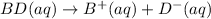
In this reaction, the complete dissociation into ions and only onside arrow represent the completely dissociated. So, it is a strong electrolyte.
(5)
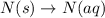
In this reaction, there is no dissociation into ions. So, It is a non-electrolyte.