Answer:
The specific latent heat of ice is approximately 341 J/g
The correct option is;
b) 341 J/g
Step-by-step explanation:
The given parameters are;
The mass of ice the pupil adds to the water, m₁ = 37 g
The initial temperature of the ice, T₁ = 0°C
The mass of the water to which the ice is added, m₂ = 100 g
The initial temperature of the water, T₂₁ = 30°C
The final temperature of the water and the melted ice, T₂₂ = 0°C
The specific heat capacity of the water, c₂ = 4.2 J/(g·°C)
By the principle of conservation of energy, we have;
The heat gained by the ice = The heat lost by the water = ΔQ₂
Given that the ice is only melted with no change in temperature, we have;
The heat gained by the ice = The latent heat needed for melting the ice
ΔQ₂ = m₂ × c₂ × (T₂₂ - T₂₁) = 100 × 4.2 × (0 - 30) = -12,600 J
The heat gained by the ice = m₁ ×
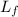
Where;
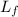 represents the specific latent heat of fusion of ice;
represents the specific latent heat of fusion of ice;
We have;
12,600 = 37 ×
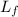
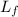 = 12,600/37 = 340.54 J/g ≈ 341 J/g
= 12,600/37 = 340.54 J/g ≈ 341 J/g
The specific latent heat of fusion of ice =
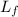 ≈ 341 J/g.
≈ 341 J/g.