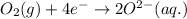Answer: The half reactions are given below.
Step-by-step explanation:
Oxidation reactions are defined as the reactions in which a chemical species looses its electrons. The oxidation state of the specie increases.
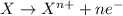
Reduction reactions are defined as the reactions in which a chemical species gains its electrons. The oxidation state of the specie gets reduced.

For the given reactions:
1.)
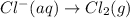
Here, the oxidation state is getting increased, therefore it is an oxidation reaction. The equation for this follows:
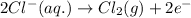
2.)
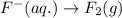
Here, the oxidation state is getting increased, therefore it is an oxidation reaction. The equation for this follows:

3.)
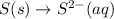
Here, the oxidation state is getting reduced, therefore it is an reduction reaction. The equation for this follows:
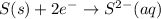
4.)
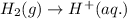
Here, the oxidation state is getting increased, therefore it is an oxidation reaction. The equation for this follows:
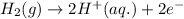
5.)

Here, the oxidation state is getting reduced, therefore it is an reduction reaction. The equation for this follows: