Answer: The new volume is 2.1 L.
Step-by-step explanation:
Use the formula Boyle's law.
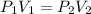
Here,
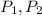 are the initial pressure and the final pressure and
are the initial pressure and the final pressure and
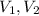 are the initial and the final volumes.
are the initial and the final volumes.
As, it is given in the problem, a helium balloon has a volume of 2.00 L at 101 kPa. As the balloon rises, the pressure drops to 97.0 kPa.
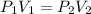
Put P_{1}=101 kPa,V_{1}=2.00L and P_{2}=97.0 kPa.
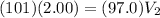
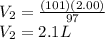
Therefore, the new volume is 2.1 L.