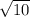Answer: The relative rate of diffusion of helium to argon is
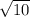
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the rate of diffusion of gas, we use Graham's Law.
This law states that the rate of effusion or diffusion of gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the molar mass of the gas. The equation given by this law follows:
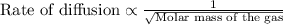
Molar mass of helium = 4 g/mol
Molar mass of argon = 40g/mol
For the rate of diffusion of helium to argon, we write the expression:
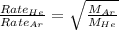
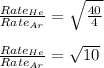
Hence, the relative rate of diffusion of helium to argon is