A reaction that results in the combining of smaller atomic nuclei is A. Fusion.
Step-by-step explanation
Atomic nuclei change only in nuclear reactions. Such reactions will alter the atom itself. In chemical reactions, nuclei stay intact. Atoms join only by the electrons outside the nuclei. Also, nuclear reactions are much more energetic.
Ionization is a chemical process. Doing so removes electrons from an atom without altering its nucleus.
Example: ionization of an H atom:
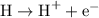
Atomic symbols stay the same in a chemical process like ionization.
In a fusion reaction, two smaller nuclei merge to produce a larger nucleus. For example, one
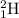 join a
join a
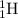 to produce one
to produce one
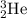 , which has more nucleons than its reactants.
, which has more nucleons than its reactants.
Example of a fusion reaction:
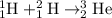 .
.
In a fission reaction, one large nuclei split into two or more smaller nuclei. For example,
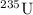 can split into
can split into
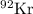 and
and
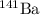 after capturing a neutron.
after capturing a neutron.
Example of a fission reaction:
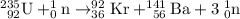 .
.
Note the change in both the atomic symbol and the atomic number in nuclear reactions.