Answer: Explained.
Step-by-step explanation: The explanations are as follows :
(7) Since GF is parallel to JK and FK and GJ are tranversals, so we have
∠GFK = ∠JKH,
∠FGK = ∠KJH (pairs of alternate interior angles) and
∠GKF = ∠JHK (vertically opposite angles).
Therefore, both the triangles are similar by AAA similarity rule.
(8) Here,
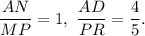
Since the ratio of the corresponding sides are not proportional, so the triangles are not similar.
(9) Here,
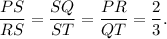
So, the triangles are similar by proportionality rule.
(10) Here,
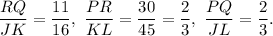
Since all the ratios are not equal, so the triangles are not similar.
(11) Here , no angle of one triangle matches with the angle of the other triangle, so the given triangles are not similar.
(12) Here,
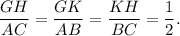
So, the triangles are similar by the proportionality rule.
Hence explained.